SdManu3 - SDPräFlexBot
Software-defined precision for highly flexible robot kinematics
In the future, the sales of electrified vehicles will increase. At the same time, changes in the legal framework and dynamic technical developments mean that only fuzzy future forecasts of customer demand are possible. To counter this tension, a change from rigid and inflexible production systems to highly flexible production systems must take place. This requires flexible software-based methodologies to increase precision.
Aim
The aim of the project is to enable simple robot kinematics for high-precision production tasks by means of high-precision optical measurement technology and software-driven adaptive accuracy-optimized configuration, path and trajectory planning.
Approach
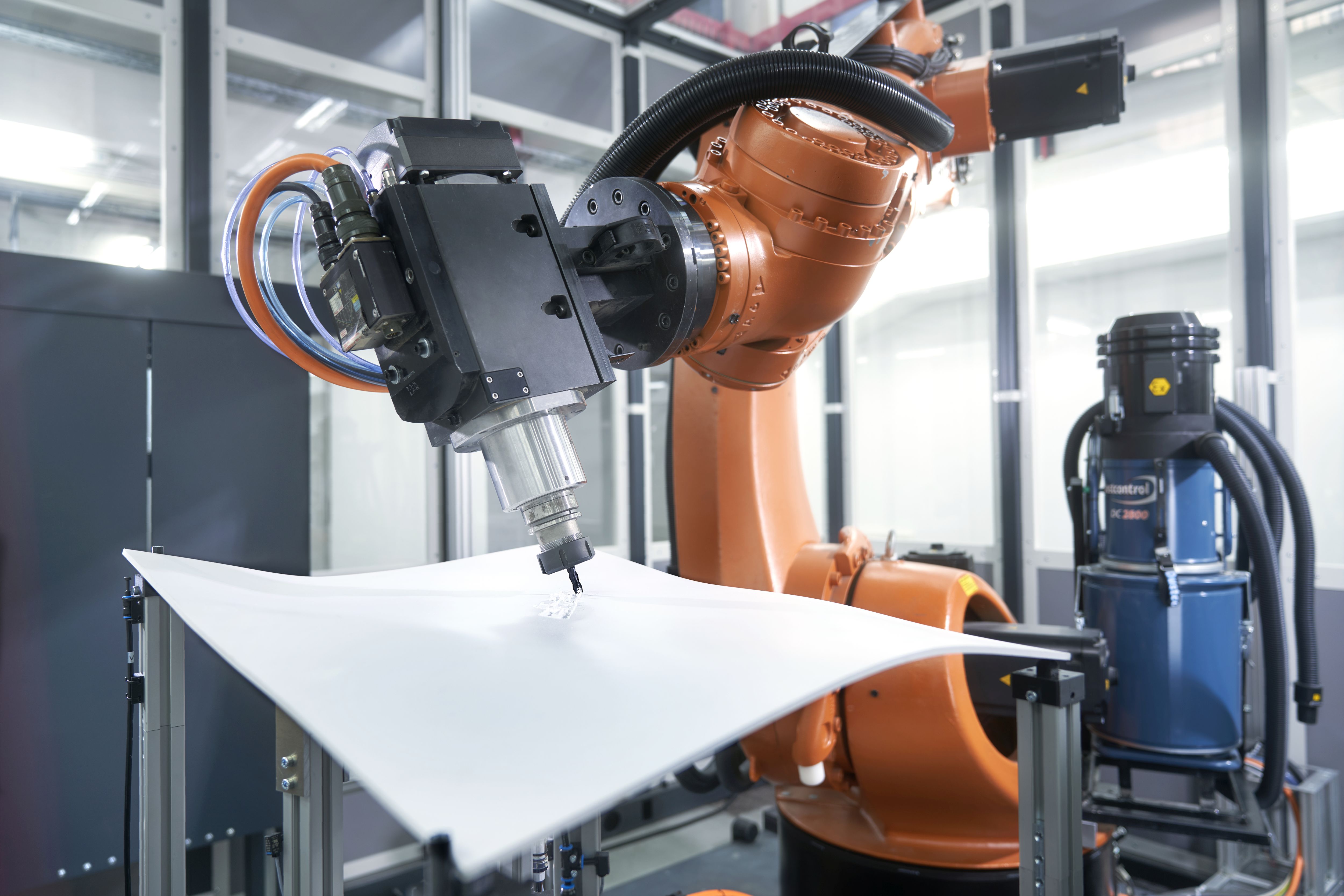
- In the current state of the art, for example in a laser welding process, a robot follows the trajectory given to it. Since it has no reference measurement of its position relative to the workpiece, the result is relatively inaccurate.
- By adding an optical measuring system, the robot's precision can be increased. However, the joints, which are controlled on the robot, themselves have only a finite precision and so there remains a variance around the target coordinates.
- To minimize the variance, an attempt is made to minimize the influence of the joint errors by using a suitable robot pose. To guarantee an optimal pose for complex weld paths, a second robot is used to reposition the workpiece.
Key data
Research Field
Software-System-ArchitecturesPeriod
01.03.2022 until 29.02.2024Project participants
- Universität Stuttgart: Institut für Systemdynamik (ISYS, Prof. Sawodny)
- Universität Stuttgart: Institut für Technische Optik (ITO, Prof. Reichelt)
- KIT: Institut für Produktionstechnik (wbk, Prof. Fleischer)
Contact

Thilo Zimmermann
Deputy Managing Director, Head of Research Coordination
- Phone
- +49 711 685 60960
- fk@icm-bw.de